Climate change poses an unprecedented challenge to Indian agriculture, threatening food security and farmer livelihoods through erratic rainfall, floods, droughts, and pest outbreaks. To build resilience, Nadia Krishi Vigyan Kendra (BCKV), West Bengal, under the jurisdiction of ICAR-Agricultural Technology Application Research Institute, Kolkata, in collaboration with the Inhana Organic Research Foundation (IORF), embarked on a pioneering journey to create a sustainable, climate-smart farming model.
The Breakthrough Achievement
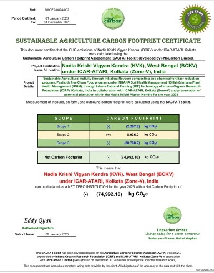
In 2025, Nadia KVK made history by becoming India’s first net-zero certified Krishi Vigyan Kendra, recognized by UK-based certifying agency i-NoCarbon Limited with a remarkable net carbon footprint of (–) 74.99 metric tonnes CO₂e.
This milestone was enabled by the MoU between ICAR-ATARI, Kolkata and IORF, which led to the development of Agriculture Carbon Footprint Assessor (ACFA) Version 1.0, India’s first indigenous carbon footprint assessment standard.
ACFA Innovation: The Make-in-India Framework
Driven by a strategic MoU between ICAR-ATARI Kolkata and the Inhana Organic Research Foundation (IORF), India pioneered its own carbon footprint assessment standard through the development of Agriculture Carbon Footprint Assessor (ACFA) Version 1.0 a Make-in-India framework tailored for diverse agro-ecosystems. Integrating international protocols, including IPCC Guidelines, GHG Protocol, ISO 14064-1, and PAS 2050, ACFA provides a realistic, holistic evaluation of agricultural carbon impacts across time horizons while aligning with India’s unique cultivation practices. This landmark achievement established a new benchmark for sustainable agriculture and reinforced the vision of self-reliant, India-specific carbon measurement standards.
Building on this foundation, ACFA Version 2.0 enhanced precision and applicability, paving the way for the Trustea Emission Calculator (TEC Tool). Leveraging ACFA 2.0, TEC not only assesses carbon footprints but also raises awareness of broader sustainability impacts, supporting initiatives such as the Regenerative Tea Initiative and demonstrating India’s leadership in climate-smart agriculture. This innovation has set a global benchmark in agricultural carbon accounting, adaptable to Voluntary Carbon Market (VCM) projects.
Pathway to Net Zero
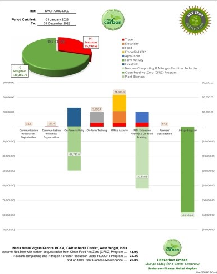
Nadia KVK achieved its net-zero certification through:
•Adoption of the Clean Food Net Zero Model with IORF, promoting pesticide-free natural farming.
•Use of Novcom compost for soil nutrient recycling, reducing urea fertilizer dependence.
•Sustainable energy and farm practices that minimized electricity and livestock-related emissions.
•Preservation of trees and perennial horticultural plants within KVK premises for effective carbon sequestration.
•Altogether, these measures resulted in a net carbon saving of 74.99 metric tonnes CO₂e.
Impact and Future Potential
Nadia KVK’s achievement goes beyond certification—it provides a replicable model for India’s 731 KVKs. The Net Zero Model, integrated with the Clean Food Net Zero (CFNZ) Program, offers transformative pathways for:
•CSR-driven sustainability initiatives.
•Net Zero compliance and carbon credit generation.
•Soil restoration and farmer livelihood security.
Validated through the IBM–IORF Sustainability Accelerator Project, this initiative stands as a first-of-its-kind effort, linking smallholder farmers with corporate sustainability goals while advancing India’s climate commitments.
Nadia KVK’s Net Zero milestone is more than an institutional achievement—it is a transformative precedent for sustainable agriculture in India. By turning vision into action, it demonstrates how innovation, partnerships, and local adaptation can lead India’s farmers toward a climate-resilient, greener future.
(Source: ICAR-Agricultural Technology Application Research Institute, Kolkata)







फेसबुक पर लाइक करें
यूट्यूब पर सदस्यता लें
X पर फॉलो करना X
इंस्टाग्राम पर लाइक करें